When I ran campaigns, I used to lament that corporations would spend more on marketing a hamburger than marketing political ideas and efforts. Back then, campaigns were struggling shoestring enterprises. No longer.
Today, campaigns and issue groups spend billions of dollars (much of it ineffectively) on communicating to voters, and fundraising at large has become big business. Ironically, the rocket fuel for all this was not the much-maligned Supreme Court decision Citizens United that gave corporations political speech rights. Rather, it was the internet – opening up a far speedier and cost-effective method of motivating voters and fundraising from them. Everything we condemn about politics and social media today – the speed of clickbait, the sensationalizing of small news events, the partisan divide – has paved the way for online fundraising and its explosive growth.
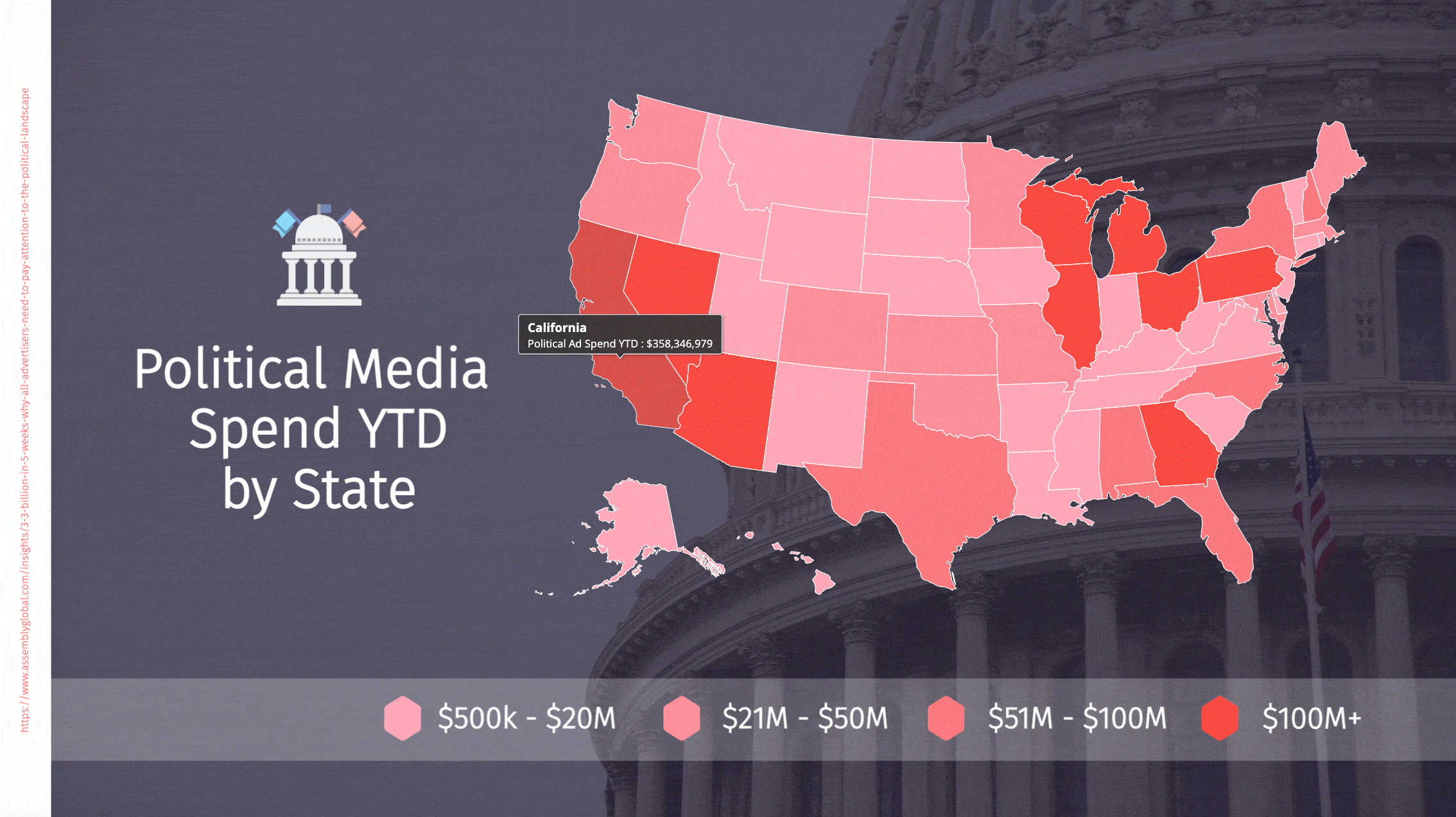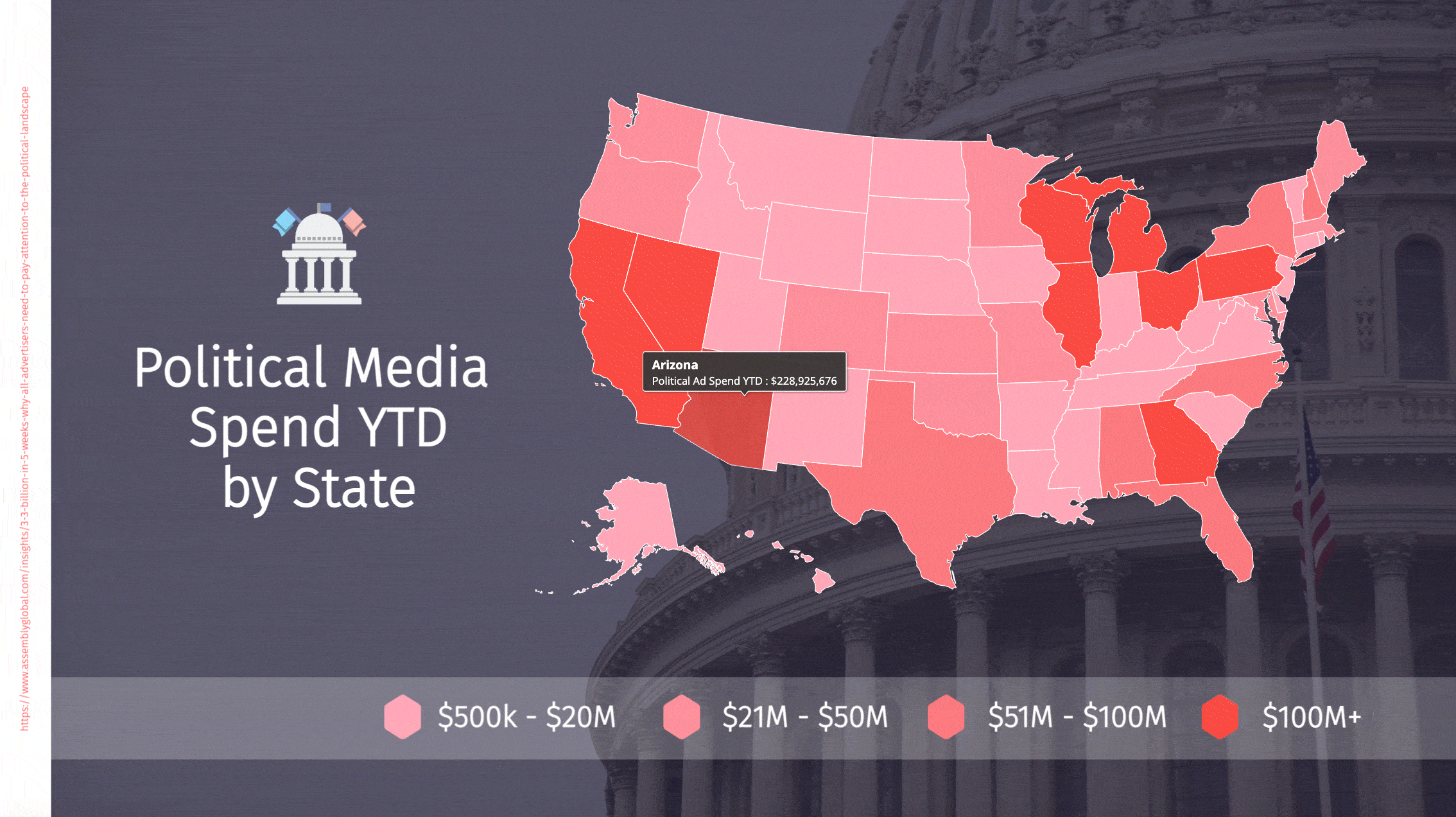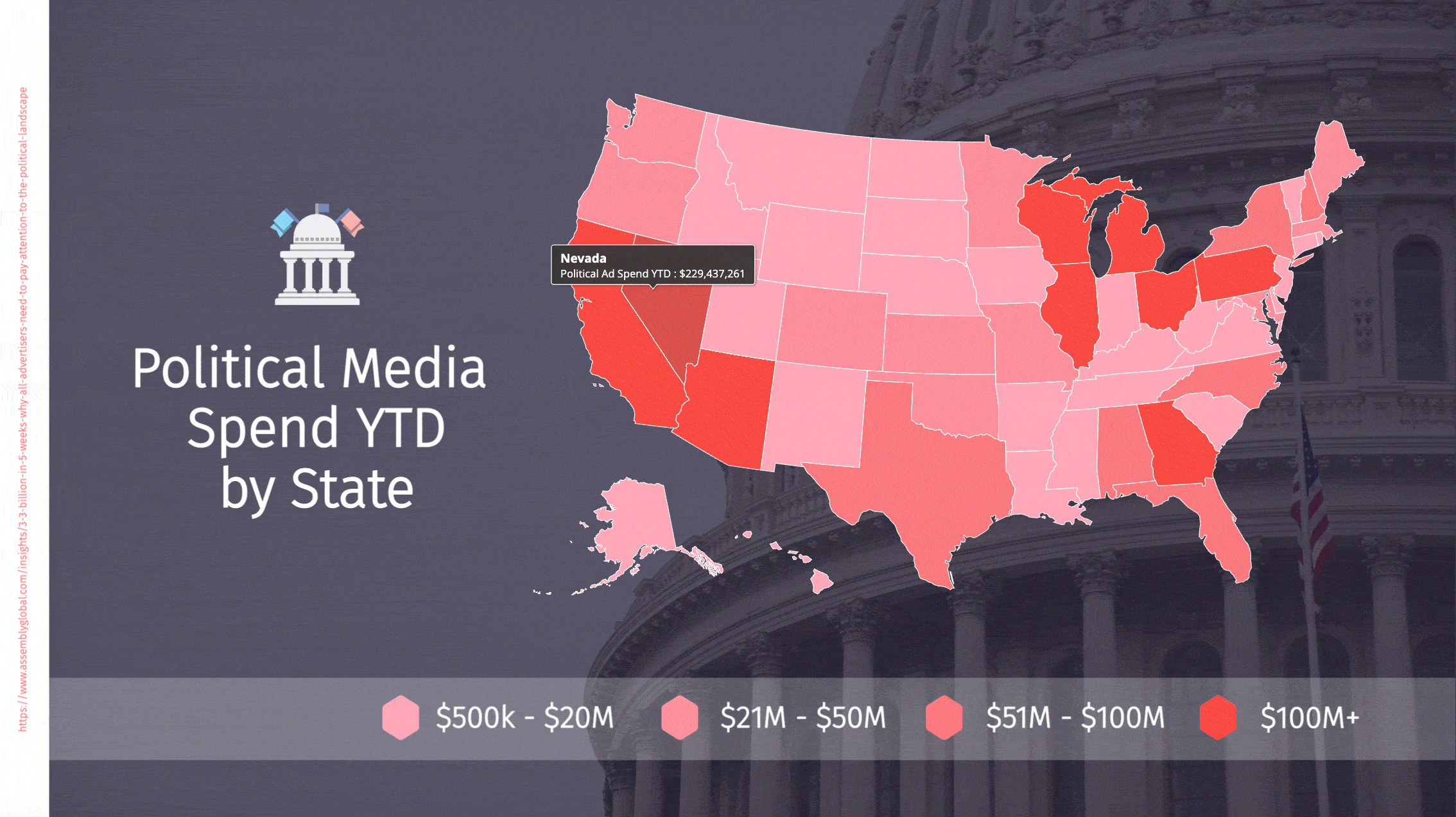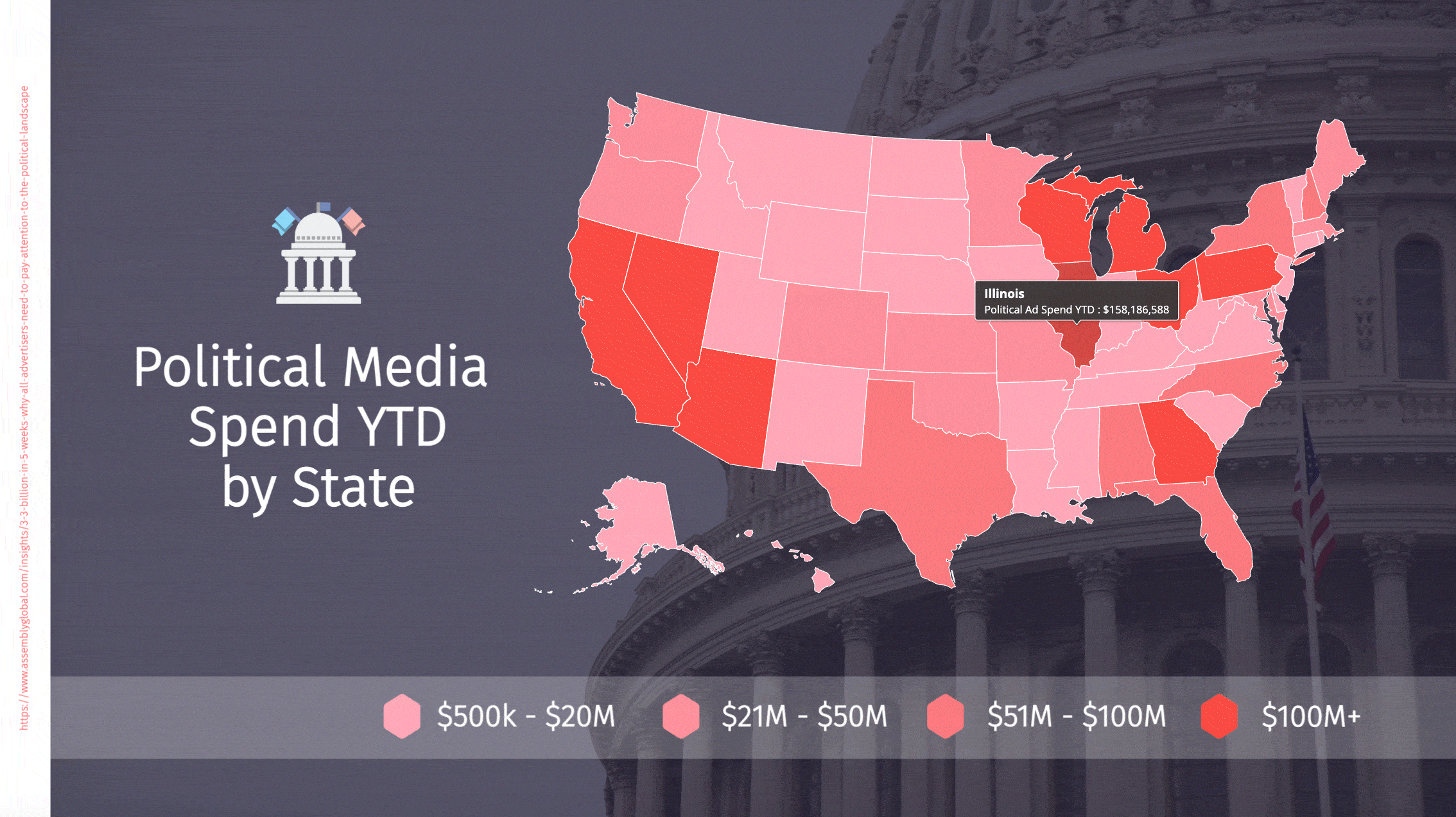
Political advertising spend is rapidly breaking records
Political advertising will hit $7.8bn in the 2022 midterm elections – nearly approaching the $8.5bn spent across TV, radio and digital media in the 2020 presidential cycle. We are seeing continued growth in campaign spending, and each mid-term is coming close to the previous presidential runs in spend. Each president leaps to a new record in political expenditures. It will take a set of really mundane candidates with a runaway winner to break this ever-increasing cycle. Absent that, this is a double-digit growth spiral for several more election cycles. I never thought I would see $10m Congressional races and $100m Senate contests, and yet those are now everyday occurrences.
Digital fundraising is rising at a faster rate than overall spending
Of the $14.4bn in paid media spent during the 2020 cycle, 49% was raised online. The 2022 cycle should exceed $14bn in paid media spend, with over 60% likely to come from online fundraising. To put that in context – in 2014, less than 9% of the $4.4bn in contributions came in via online donors. Democrats, who are notably vocal about money in politics, spend the most – generally about 50% more than the Republicans.
Donors today are largely first-timers – and start small
For most donors over the last few cycles, giving to politics has been a new experience. Most of these contributions aren’t from big-dollar donors or PACs, but low-dollar donations from average Americans giving amounts between $30 and $100 (76.1% of Act Blue Democratic donors in 2020 were first-time donors).
Americans have a love-hate relationship with political giving. When asked to give $1 on their tax return to fund campaigns, most Americans said ‘no’ to the voluntary check-off, and the fund was running out of money. Taxpayers generally believed politicians should finance their own campaigns and leave the public out of them. In the ‘70s and ‘80s, candidates used direct mail to gather low-dollar gifts, but it was slow and expensive. In 2008, social media entered the scene and spilled over into news and politics. With its proliferation of inflammatory messages and clickbait, social media was the ideal incubator for online giving. While less than 1% of voters donated to campaigns in the past, that number is now up to 10% and continues to grow.
How companies can mimic political fundraising techniques
I always call online fundraisers the best marketers in the world. Why? Because in return for their funds, consumers get absolutely nothing of tangible value – no product and not even a tax deduction.
What makes them such good marketers? They believe in math. They have hundreds of people who craft messages, then test them methodically and go big with the ones that work. They refine their lists, carefully managing their communications to people to avoid overload or confusing and contradictory messages. And they utilize low-cost, effective messaging techniques, driving campaigns through email and increasingly via text messaging, as consumers switch their preferred communication modes.
Today, these fundraisers employ the process and rigor that most corporations should envy: ample message creation, thorough testing, careful media mix modeling and rigorous adherence to performance standards and return on investment. Politics once again leads the way in how to structure and carry out effective online marketing. This rigorous approach would and is working for commercial online marketing, though retail marketers have more limits on how aggressive they can be. Still, they can treat Thanksgiving, Prime Days and Christmas as a kind of commercial election day, working up to harvesting sales in the same way that political fundraising is mostly prospecting until the campaign’s final months. Commercial marketers can also be more aggressive via text messaging to mimic these successful political messages.
Political fundraising is only starting to hit its groove and has many potential roads for broad expansion. While online fundraising exploded in 2020, only 20% of the 180 million Americans who voted in that cycle donated to a campaign, and under 2% of the country gave over $200. By comparison, over 70% of Americans gave to charity in 2020, totaling $324.1bn in individual contributions that mirror the scale and spend of small-dollar political contributions. The addressable digital advocacy and political fundraising markets represent massive growth opportunities.
Galvanizing the masses around a cause: still the mandate
Online political fundraising is, in essence, fan marketing. It’s about getting those who care most about your brand to be even more passionate and committed. When an employee of a competitor company insults a customer, don’t just sit there – use it to your advantage and broadcast it to your loyal fans. Most commercial marketing, even online, is passionless and saccharine; if you want to be as successful as political marketers, you will have to take some risks and be bolder. Now, this may not fit all corporate brands, but that’s the advantage that upstart challenger brands have in the marketplace – they can be free to be out there, within the bounds of good humor and taste.
To be clear, political ads continue to be a discipline unto themselves, built primarily around negative messages with no clear analog in commercial marketing. Online fundraising also includes tough negative messages, but is built mainly around bringing people together as part of a group that wants to help a cause. This new technique is at the forefront of what’s possible in this new online world as more and more people are plugged into news and current events. Online fundraising can and will expand into the not-for-profit world, but it will surely lead the way in fan marketing for breakthrough companies as well.
Mark Penn is chairman and chief executive officer of New York-based marketing group Stagwell.